Solid geometry
round, sphere
Procedure: Radius of circumscribed sphere
1
\( R^2 = \frac{1}{4} h^2 + r^2 \)
Proof for example:
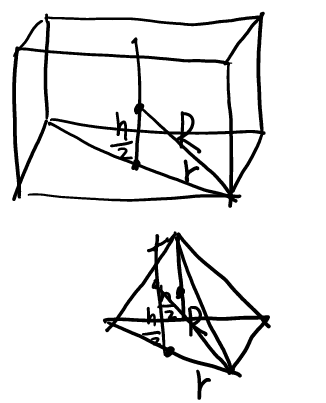
2
\( R = \frac{l^2}{2} \)
Proof for example:
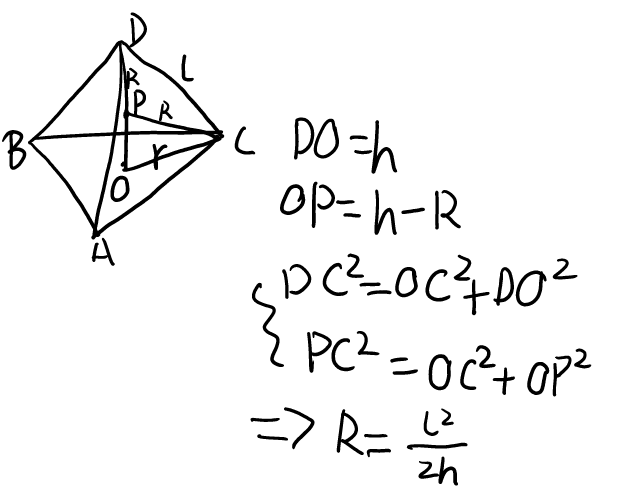
Mnemonic: 两只老虎
Tetrahedron
Opposite sides are equal
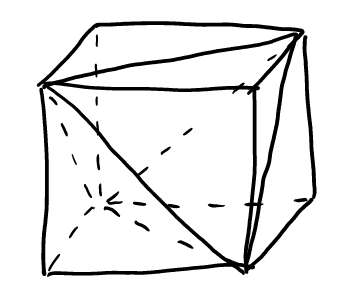
NCEE

Inscribed sphere of a Pyramid
\( R = \frac{3V}{S} \)
Regular tetrahedron with edge length \( a \): \( R = \frac{\sqrt{6}}{12} a \)
normal vector
Procedure: intercept
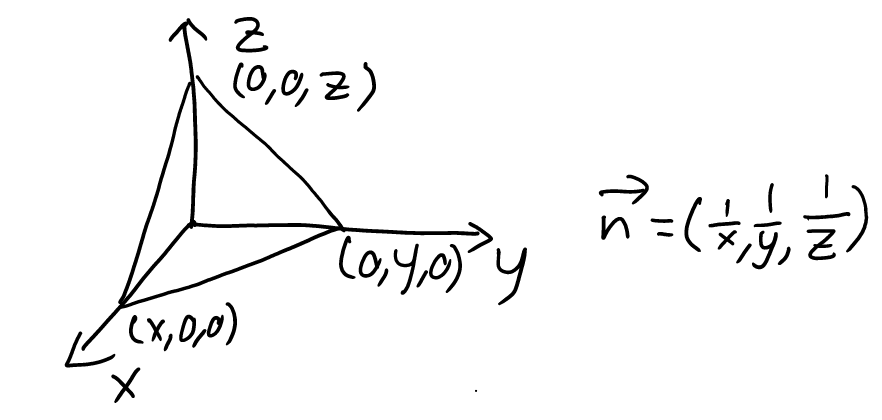
No intersection: For example, \( n = (0, y, z) \) if and only if there is no intersection between the plane and the x-axis.
Procedure: Point-to-Plane Distance
\( \frac{\vec{v}\vec{n}}{\left\lvert n \right\rvert} \)
Procedure: Pyramid Projection
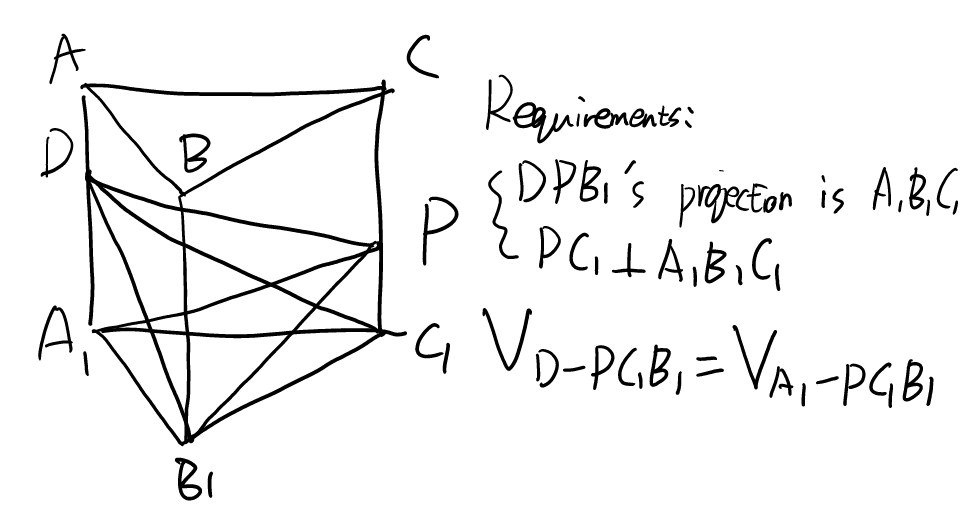
Note: The side edge is perpendicular to the projection surface.
NCEE
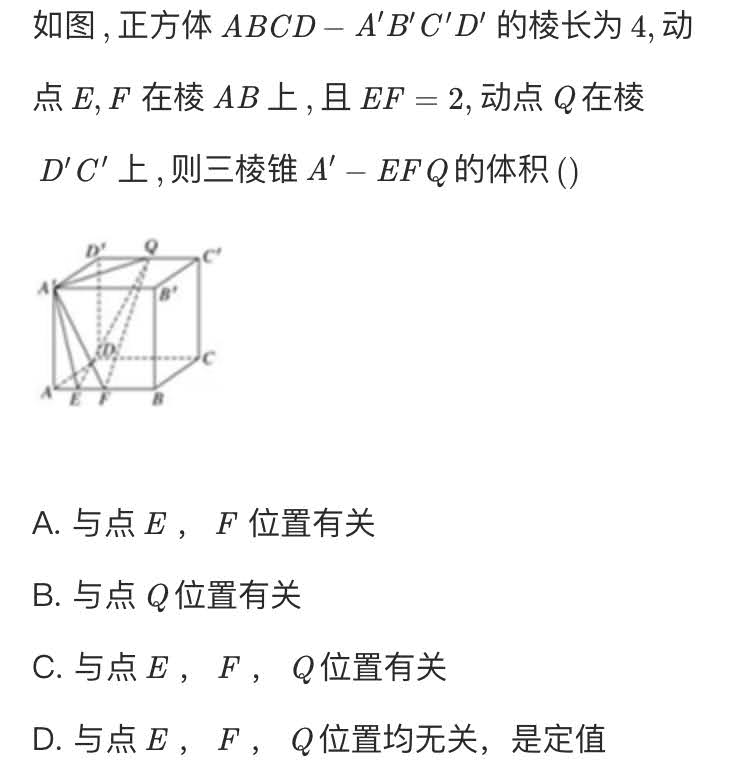
Theorem 0
(need more study)
\(sin\alpha=sin\beta\cdot\sin\gamma\) \(\alpha\) 线面 \(\beta\) 锐二面角 \(\gamma\) 线与交线夹角
Statistical Theorem 1
\(V=\frac{4}{3}\pi R^3\)
In general, the radius of the ball is regular which means that radius won't be something like \(\sqrt[3]{\text{...}}\)
NCEE
